首页 > NEWS > Company News
【summary】
Plastics are widely used in medical devices, automobiles and daily products due to their advantages such as light weight, good impact resistance, good transparency, good insulation, good formability, good colorability and low processing cost. The final performance of plastic parts mainly depends on the connection method between plastic parts.
Plastics have many advantages such as light weight, good impact resistance, good transparency, good insulation, good formability, good colorability, and low processing cost, so they are widely used in medical devices, automobiles, and daily products. The final performance of plastic parts mainly depends on the connection method between plastic parts. After long-term research and practice, scientists and related engineering and technical personnel have developed many different plastic connection methods. This article briefly introduces these plastic connection technologies, hoping to provide a reference for designers in related fields to choose plastic connection methods.
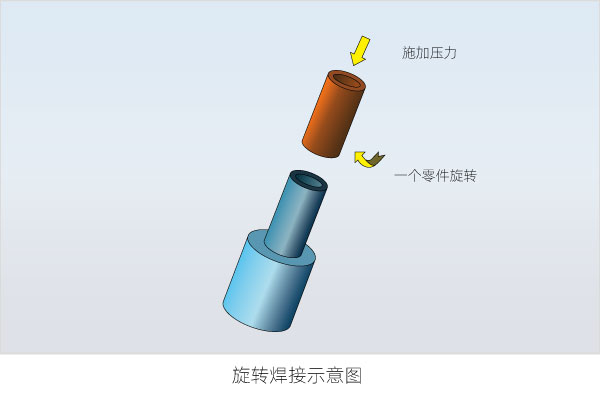
13. Rotary welding
Rotary friction plastic welding machines are generally used to weld two circular thermoplastic workpieces. During welding, one workpiece is fixed on the bottom mold, and the other workpiece rotates on the surface of the fixed workpiece. Because both workpieces have a certain pressure effect, the heat generated by the friction between the two workpieces can melt the contact surfaces of the two workpieces to form a closed combination. Among them, the positioning rotation is to rotate within the set time, stop at the set position instantly, and become permanently melted.
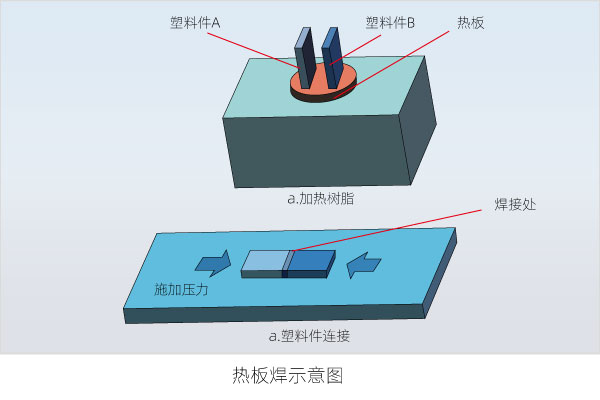
14. Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate welding refers to placing the edges of the two plastic parts to be connected on a thermostat-controlled hot plate and heating them until the surface melts, and then pressing the two softened surfaces together with a small pressure to achieve the connection of the plastic parts, as shown in the figure. In addition, there is a common hot plate heat sealing technology. First, the two parts to be connected are stacked together, the heat sealing plate is heated by an electric heating tube, and the heat sealing plate is lowered to the upper part of the two parts, while applying a certain amount of pressure to the heat sealing plate. The heat sealing plate melts the contact area of the two parts, and then solidifies and connects them together. This technology is mainly used for the sealing connection of polymer resin film materials and plastic parts.
15. Hot gas welding
There are three methods of hot air welding: spot welding, permanent hot air welding and extrusion welding. Their basic principles are the same. The heat generated by the heating wire is taken away by the wind generated by the motor, so as to obtain flowing hot air, so that the two plastic parts to be welded are heated and bonded with the welding rod in a molten state, thereby achieving the purpose of welding. Among them, spot welding is used to fix all parts together before permanent welding. Spot welding is a temporary welding material that can be completed without welding rods, and a spot welding nozzle is required.
Permanent welding should use welding rods of the same material as the parts to be welded. The welding nozzle moves back and forth quickly in a fan shape in the welding area, usually pressed together with a hot roller until the V-groove and the welding rod soften to the point where they can be welded. Extrusion welding refers to feeding from a hopper in the form of granules or in the form of welding rods on a cylinder, then extruding from a single screw melting chamber driven by a motor, heating with an electric heating coil or hot air, heating the joint surface with a hot air preheater connected to the extruder, and finally melting the resin and the welded parts together.
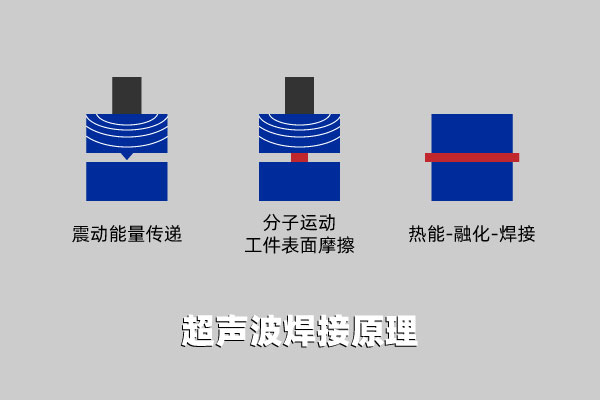
16. Ultrasonic welding
Ultrasonic welding is the conversion of 50/60Hz current into 15, 20, 30 or 40KHz electrical energy through an ultrasonic generator. The converted high-frequency electrical energy is fed into the transducer, converted again into mechanical motion of the same frequency, and then transmitted to the welding head through a set of adjustable horn devices. The welding point will receive the vibration energy and transmit it to the joint of the workpiece. In this area, the vibration energy is converted into heat energy through friction, causing the contact surface of the two plastics to melt rapidly, and a certain amount of pressure is added to make them melt into one. When the ultrasonic wave stops, the pressure will continue to act for a few seconds, causing the material to solidify, shape, and form a strong molecular chain, thereby achieving the initial welding strength and film strength.
The key components of the ultrasonic welding system include the ultrasonic generator, converter/amplitude regulator/welding head, mold and frame. The quality of the ultrasonic plastic welding machine depends on the amplitude, pressurization and welding time of the transducer welding head. The welding time and welding head pressure can be adjusted, and the amplitude is determined by the transducer and horn.
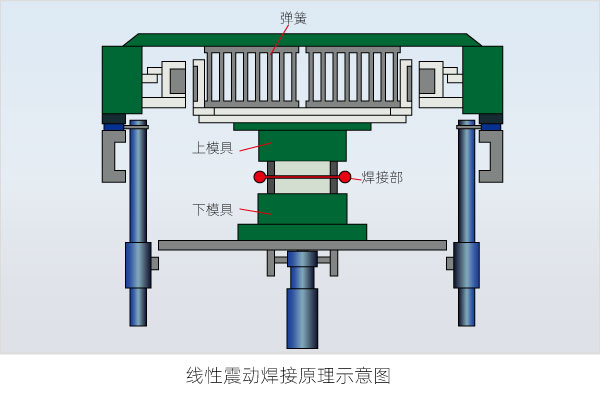
17. Vibration welding
The vibration welding process has six process parameters: welding time, holding time, welding pressure, amplitude, frequency and voltage. Vibration welding is divided into linear vibration welding, orbital vibration welding and angle vibration welding.
The linear vibration friction welding machine uses the friction heat energy generated by the contact surface of the two workpieces to be welded to melt the plastic. The heat energy comes from a certain pressure, and one workpiece moves back and forth on the other surface with a certain displacement or amplitude. Once the desired welding level is reached, the vibration will stop, and a certain pressure will still be applied to the two workpieces to cool and solidify the just welded parts to form a tight bond.
Orbital vibration friction welding is a method of welding that uses frictional heat energy. During orbital vibration friction welding, the upper workpiece performs orbital motion at a fixed speed - circular motion in all directions. The motion can generate heat energy, which can bring the welding parts of the two plastic parts to the melting point. Once the plastic begins to melt, the motion will stop and the welding parts of the two workpieces will solidify and firmly connect together. The small clamping force will cause minimal deformation of the workpiece, and workpieces with a diameter of less than 10 inches can be welded with orbital vibration friction.
Angle vibration welding refers to the rotational motion of the workpiece around a fulcrum. Currently, there are few commercially produced angle vibration welding machines.
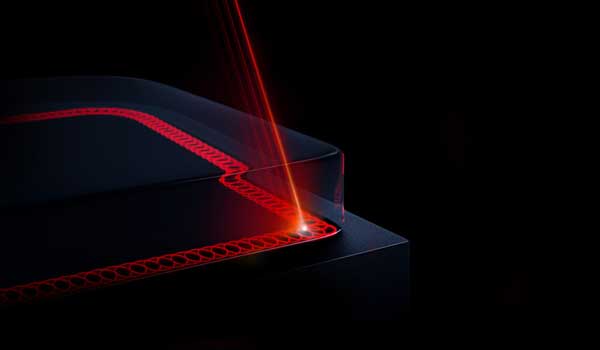
18. Laser welding
Plastic laser welding technologyThe high temperature caused by the laser beam melts the contact part of the plastic and combines thermoplastic sheets, films or plastic parts to achieve bonding. The technology first appeared in the 1970s, but due to its high cost, it could not compete with early plastic bonding technologies such as vibration welding and hot plate welding. However, since the mid-1990s, the technology has gradually become widely popular due to the reduction in the cost of equipment required for laser welding technology.
Laser welding technology can play a big role when the plastic parts being bonded are very delicate materials (such as electronic parts) or require a sterile environment (such as medical devices and food packaging). Laser welding technology is fast and is particularly suitable for assembly line processing of automotive plastic parts. In addition, laser welding technology can be used for complex geometries that are difficult to bond using other welding methods.
The main advantages of laser welding are that the welding equipment does not need to come into contact with the plastic parts being bonded; it is fast; the equipment is highly automated, making it easy to process complex plastic parts; there is no flash; the welding is strong; high-precision welded parts can be obtained; there is no vibration technology; it can produce airtight or vacuum-tight structures; it minimizes thermal damage and thermal deformation; and resins of different compositions or colors can be bonded together.
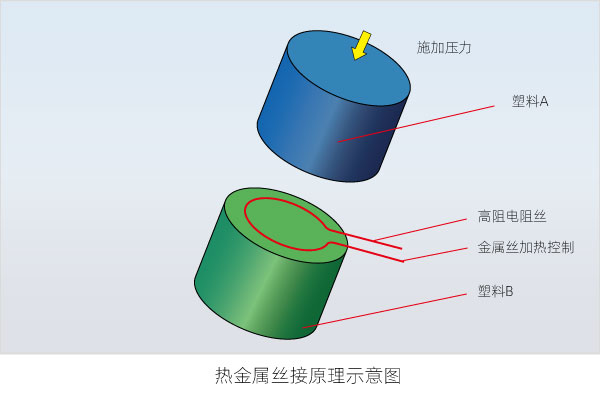
19. Hot wire welding
Hot wire welding, also known as resistance welding, uses a metal wire to transfer heat between the two connected plastic parts, melting the surface of the plastic parts and applying a certain pressure to connect them together.
Place the metal wire on one surface of the connecting parts. When current passes through the metal wire, the metal wire is heated by its resistance and transfers the heat to the plastic part. After welding, the metal wire remains in the plastic product, and the part that extends beyond the connection is cut off after welding. Generally, grooves or other positioning structures are designed on the parts to ensure that the metal wire is in the right position.
| Free solutions/free proofing 13710252340
Previous: What are the welding methods f
Next:None